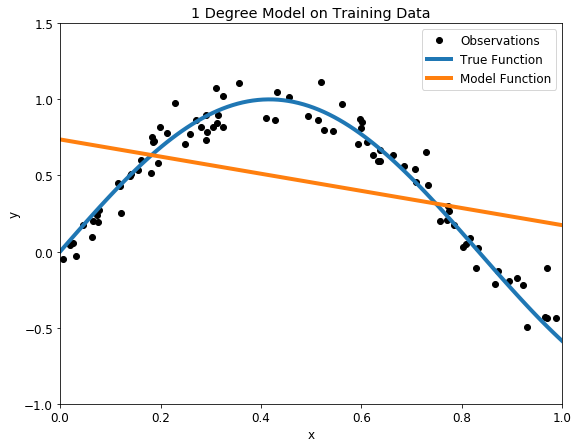
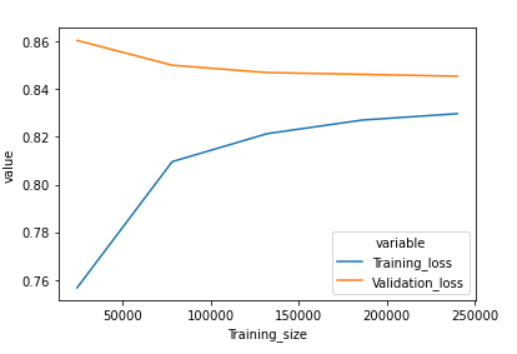
UNDERFIT and OVERFIT Explained. The main aim here is to find the best…, by Aarthi Kasirajan
4.9 (119) · $ 15.50 · In stock
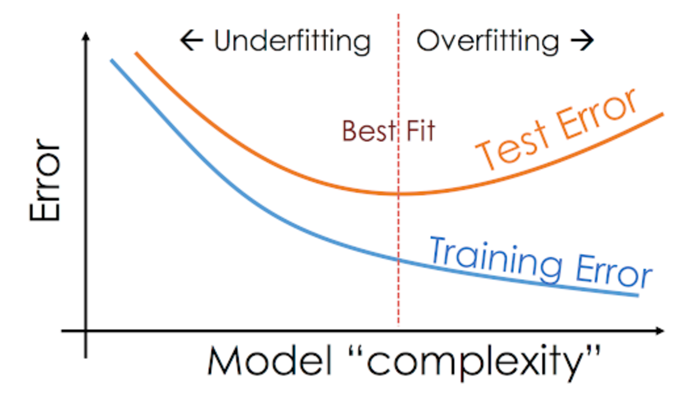
The main aim in any model is to find the best fit line that satisfies most (if not all ) data points given in the dataset. In a Regression model(for this case), the main aim here is to find the best…
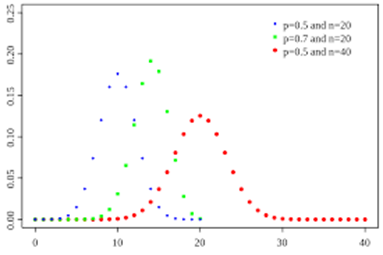
Data Distribution Types. A data distribution is a function which
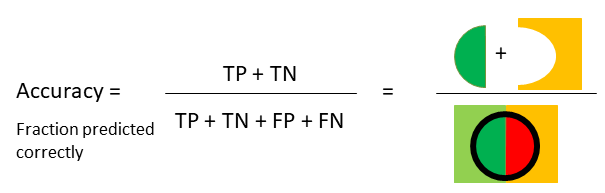
Logistic Regression Part 2: Error Metric
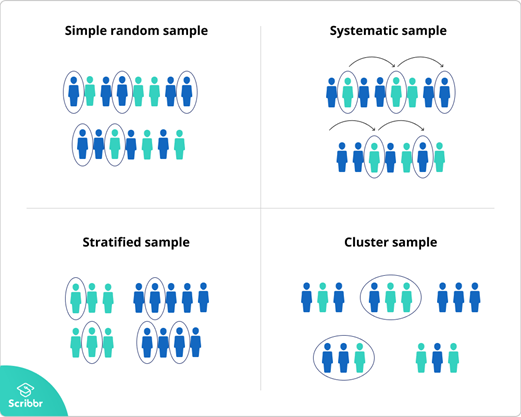
Probability Sampling Methods Explained, by Aarthi Kasirajan
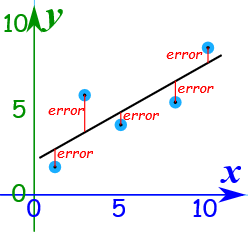
Linear Regression using Sum of Least Squares
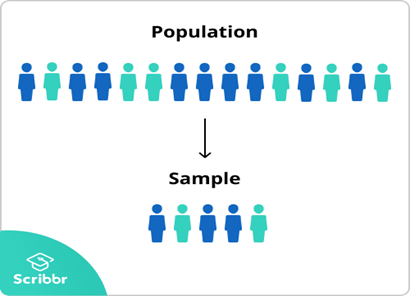
Probability Sampling Methods Explained, by Aarthi Kasirajan

UNDERFIT and OVERFIT Explained. The main aim here is to find the
Logistic Regression Explained :Part 1, by Aarthi Kasirajan
LASSO Regression In Detail (L1 Regularization)
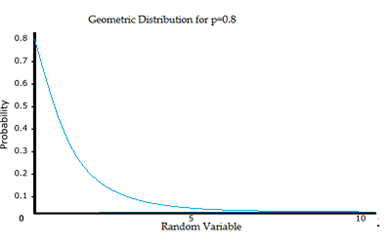
Data Distribution Types. A data distribution is a function which
Data Distribution Types. A data distribution is a function which
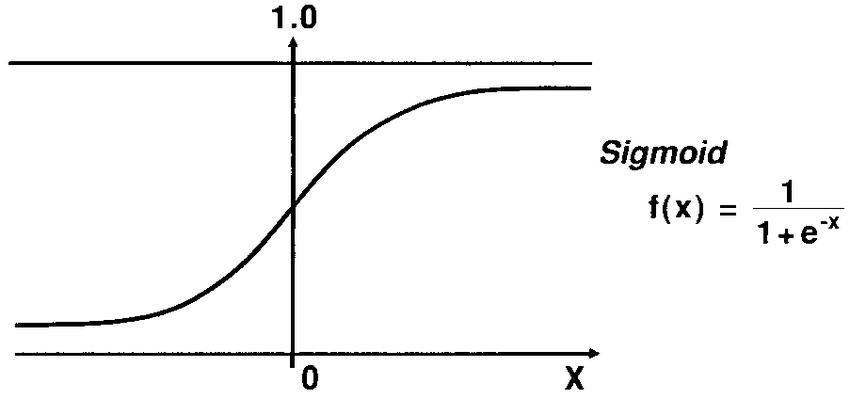
Logistic Regression Part 2: Error Metric
Logistic Regression Part 2: Error Metric